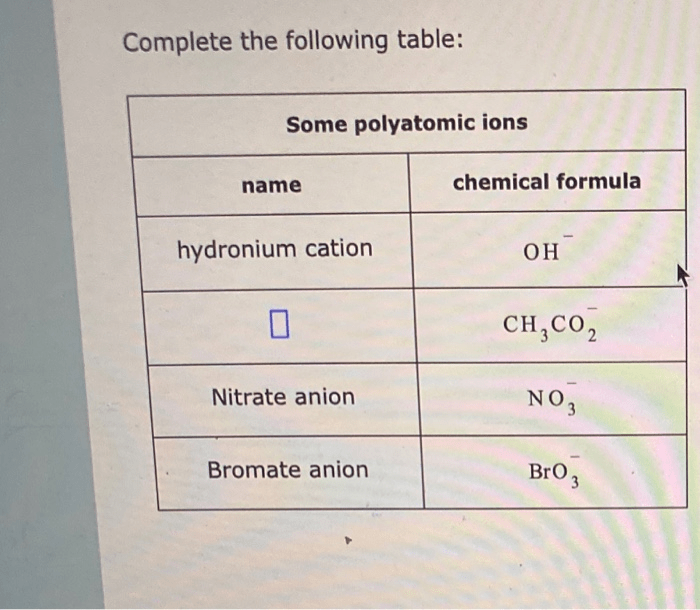
Complete the following table some polyatomic ions name chemical formula – Embark on a comprehensive exploration of polyatomic ions, their structure, properties, and significance in various scientific disciplines. This article delves into the intricacies of polyatomic ions, providing a thorough understanding of their composition, naming conventions, and applications.
Polyatomic ions, composed of multiple atoms covalently bonded together and carrying a net electrical charge, play a crucial role in various chemical processes. Understanding their properties and behavior is essential for comprehending the fundamental principles of chemistry.
Introduction to Polyatomic Ions: Complete The Following Table Some Polyatomic Ions Name Chemical Formula
Polyatomic ions are charged chemical species composed of two or more atoms that are covalently bonded. They exhibit a net electrical charge and behave as single units within chemical reactions.
The structure of polyatomic ions varies depending on the specific atoms involved and their arrangement. They can be linear, bent, or have more complex geometries. The properties of polyatomic ions, such as their solubility, acidity, and reactivity, are determined by their composition and structure.
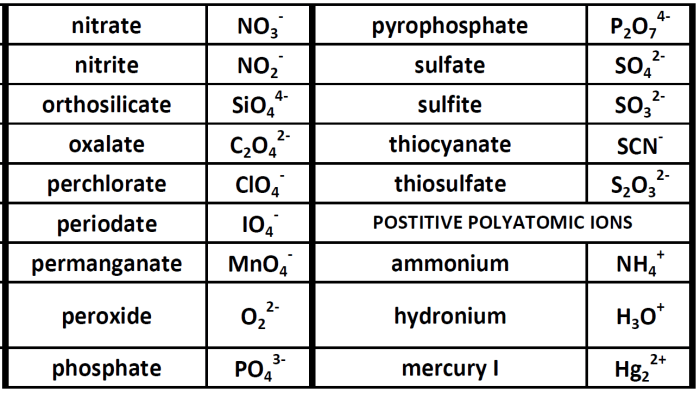
Table of Polyatomic Ions
| Name of the Ion | Chemical Formula | Charge | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ammonium | NH4+ | +1 | NH4Cl, (NH4)2SO4 |
| Hydroxide | OH– | -1 | NaOH, KOH, Ca(OH)2 |
| Nitrate | NO3– | -1 | NaNO3, KNO3, Ca(NO3)2 |
| Sulfate | SO42- | -2 | Na2SO4, K2SO4, CaSO4 |
| Carbonate | CO32- | -2 | Na2CO3, K2CO3, CaCO3 |
| Phosphate | PO43- | -3 | Na3PO4, K3PO4, Ca3(PO4)2 |
Identifying Polyatomic Ions
Polyatomic ions can be identified in chemical formulas by their characteristic suffixes. These suffixes indicate the charge of the ion:
- -ate: -2 charge (e.g., sulfate, nitrate)
- -ite: -1 charge (e.g., nitrite, sulfite)
- -ide: -1 charge (e.g., chloride, oxide)
Naming Polyatomic Ions
Polyatomic ions are named using the following rules:
- The root of the name is based on the element present in the ion.
- The suffix -ate is used for ions with a -2 charge.
- The suffix -ite is used for ions with a -1 charge.
- The suffix -ide is used for ions with a -1 charge.
- Prefixes such as di-, tri-, tetra-, and penta- are used to indicate the number of atoms of the element present in the ion.
Writing Chemical Formulas with Polyatomic Ions, Complete the following table some polyatomic ions name chemical formula
When writing chemical formulas with polyatomic ions, it is important to ensure that the overall charge of the compound is balanced. This can be achieved by combining the appropriate number of cations and anions.
For example, to write the chemical formula for sodium sulfate, we combine the sodium cation (Na +) with the sulfate anion (SO 42-). Since the sulfate anion has a charge of -2, we need two sodium cations to balance the charge, resulting in the formula Na 2SO 4.
Applications of Polyatomic Ions
Polyatomic ions play a crucial role in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and environmental science.
- In chemistry, polyatomic ions are used as ligands in coordination complexes and as counterions in ionic compounds.
- In biology, polyatomic ions are essential for maintaining pH balance and cellular function. For example, the bicarbonate ion (HCO 3–) helps to regulate pH in the blood.
- In environmental science, polyatomic ions are involved in processes such as acid rain and water pollution. The nitrate ion (NO 3–) can contribute to eutrophication, while the sulfate ion (SO 42-) can form acid rain.
Questions and Answers
What are polyatomic ions?
Polyatomic ions are groups of atoms that carry a net electrical charge and behave as a single unit within chemical compounds.
How are polyatomic ions named?
Polyatomic ions are named based on the elements they contain and their charge. The suffix “-ate” is used for ions with a negative charge, while “-ite” is used for ions with a lower negative charge.
What are some common examples of polyatomic ions?
Common examples of polyatomic ions include hydroxide (OH-), sulfate (SO42-), and nitrate (NO3-).