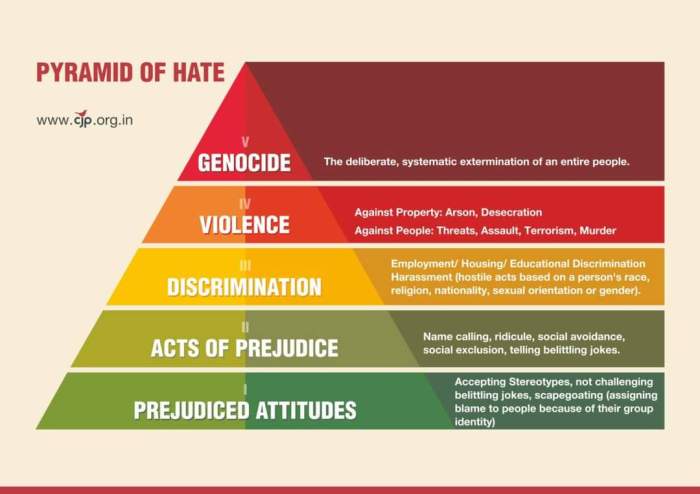
Discriminatory acts are always accompanied by prejudiced attitudes, a pervasive and pernicious reality that profoundly shapes our social fabric. Prejudice, a deeply held negative attitude towards a group of people, manifests itself in discriminatory behavior, creating a cycle of inequality and injustice.
The relationship between prejudice and discrimination is undeniable, with prejudice providing the ideological foundation for discriminatory acts. From subtle biases to overt acts of hate, prejudice permeates all levels of society, influencing our interactions, decisions, and access to opportunities.
Prejudice and Discrimination: Exploring the Interconnection
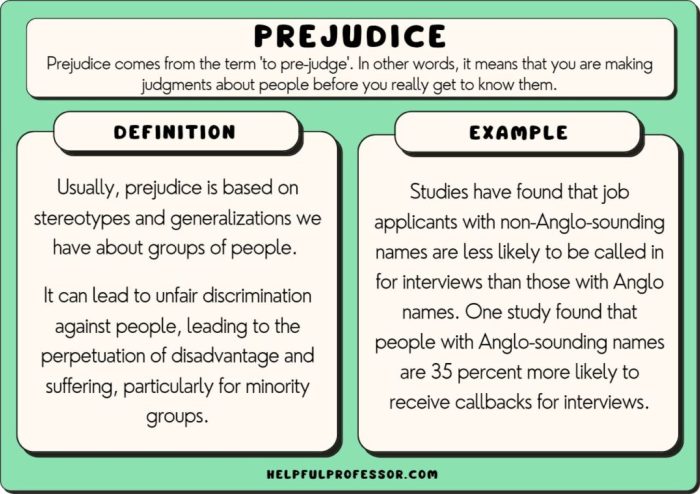
Prejudice and discrimination are inextricably linked phenomena that perpetuate social inequality. Prejudice refers to negative attitudes and beliefs held against individuals based on their perceived membership in a particular group, while discrimination involves actions that disadvantage or limit opportunities for these individuals.
Prejudice often manifests in discriminatory behavior, such as biased hiring practices, unequal access to education, and differential treatment in the criminal justice system. These actions stem from psychological and social factors, including cognitive biases, stereotypes, and a desire to maintain group superiority.
Unconscious Bias and Implicit Prejudice, Discriminatory acts are always accompanied by prejudiced attitudes
Unconscious bias and implicit prejudice are subtle forms of prejudice that operate outside of conscious awareness. These biases can influence discriminatory acts even when individuals do not consciously intend to harm or disadvantage others.
Strategies for mitigating unconscious bias include self-reflection, training, and exposure to diverse perspectives. By acknowledging and challenging our own biases, we can reduce their impact on decision-making.
Intersectionality of Prejudice and Discrimination
Prejudice and discrimination often intersect with other forms of oppression, such as racism, sexism, and classism. Marginalized groups experience multiple layers of discrimination, which can compound its negative effects.
For example, women of color may face discrimination based on both their race and gender, which can limit their access to employment, housing, and healthcare.
Legal and Ethical Implications of Discriminatory Acts
Discriminatory acts have serious legal consequences, as they violate both national and international laws. Ethical obligations also compel us to prevent and address discrimination, as it undermines human dignity and social justice.
Landmark discrimination cases have established legal precedents that protect individuals from unfair treatment based on protected characteristics, such as race, religion, and gender.
Strategies for Combating Prejudice and Discrimination
Combating prejudice and discrimination requires multifaceted strategies that address both individual and societal factors. Effective strategies include:
- Educational campaigns to promote understanding and empathy
- Community dialogues to address issues of bias and discrimination
- Training programs to raise awareness of unconscious bias
- Policy changes to create inclusive environments
Creating Inclusive Environments
Creating inclusive environments is essential for fostering diversity and reducing discrimination. Best practices include:
- Establishing clear policies against discrimination
- Providing training on diversity and inclusion
- Encouraging open communication and dialogue
- Supporting employee resource groups and affinity networks
By promoting inclusivity, organizations can create workplaces and communities where all individuals feel valued and respected, regardless of their differences.
General Inquiries: Discriminatory Acts Are Always Accompanied By Prejudiced Attitudes
What are the key factors that contribute to prejudice?
Prejudice is often rooted in fear, ignorance, and a lack of exposure to diverse perspectives.
How can unconscious bias influence discriminatory acts?
Unconscious bias refers to implicit attitudes and stereotypes that can influence our thoughts and behaviors without our conscious awareness, leading to discriminatory practices.
What are the legal consequences of discriminatory acts?
Discrimination is illegal in many countries, with laws protecting individuals from discrimination based on race, gender, religion, and other protected characteristics.