Amoeba sisters video recap answers dna vs rna – Embarking on an educational journey, this article delves into the intriguing world of DNA and RNA, guided by the insights from the Amoeba Sisters video. As we unravel the intricacies of these fundamental molecules, we will explore their structures, functions, and the significance of transcription and translation in protein synthesis.
Through a comprehensive examination of the Amoeba Sisters video recap, we will shed light on the key distinctions between DNA and RNA, highlighting their unique characteristics and the impact they have on cellular processes.
DNA vs RNA Structures
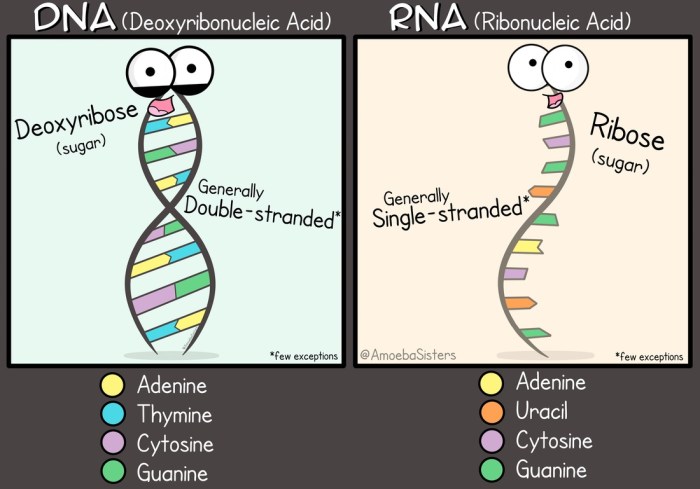
DNA and RNA are two essential molecules that play crucial roles in the storage and expression of genetic information. They share some structural similarities, but also exhibit key differences that impact their functions.
| Characteristic | DNA | RNA |
|---|---|---|
| Sugar-phosphate backbone | Deoxyribose sugar with phosphate groups | Ribose sugar with phosphate groups |
| Nitrogenous bases | Adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), cytosine (C) | Adenine (A), uracil (U), guanine (G), cytosine (C) |
| Double-stranded or single-stranded | Double-stranded (double helix) | Single-stranded (can form temporary base-pairing) |
| Location in the cell | Nucleus, mitochondria | Nucleus, cytoplasm |
The double-stranded nature of DNA provides stability and protection for the genetic code. RNA, on the other hand, is single-stranded and more flexible, allowing it to participate in various cellular processes, including protein synthesis.
Transcription and Translation

Transcription and translation are two essential processes that enable the expression of genetic information from DNA to proteins.
Transcriptionis the process of copying the genetic information from DNA into a complementary RNA molecule. It occurs in the nucleus and is carried out by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. The resulting RNA molecule, known as messenger RNA (mRNA), carries the genetic code to the cytoplasm.
Translationis the process of converting the genetic code in mRNA into a protein. It occurs on ribosomes in the cytoplasm. During translation, transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules bring specific amino acids to the ribosome, where they are linked together to form a polypeptide chain, which eventually folds into a functional protein.
Transcription and translation are crucial processes for the production of proteins, which are essential for virtually all cellular functions.
Amoeba Sisters Video Recap

The Amoeba Sisters video on DNA vs RNA provides a clear and engaging overview of the differences between these two molecules.
Key Points Covered:
- The structural differences between DNA and RNA, including the sugar-phosphate backbone, nitrogenous bases, and double-stranded vs. single-stranded nature.
- The roles of DNA and RNA in transcription and translation.
- The importance of transcription and translation for protein synthesis.
The video effectively clarifies the complex topic of DNA vs RNA by using simple language and vivid animations.
Applications of DNA and RNA
DNA and RNA have a wide range of practical applications in fields such as medicine and biotechnology.
Medical Applications:
- Genetic testing: DNA analysis can be used to identify genetic disorders and predict disease risk.
- Disease diagnosis: RNA analysis can be used to detect the presence of viruses or bacteria in the body.
- Gene therapy: DNA can be used to introduce new genes into cells to treat genetic disorders.
Biotechnology Applications:
- Biofuels: RNA can be used to produce biofuels from renewable resources.
- Vaccines: RNA can be used to develop vaccines against viruses and other diseases.
- Gene editing: DNA editing techniques, such as CRISPR-Cas9, allow for precise changes to DNA, enabling the development of new therapies and treatments.
The potential of DNA and RNA in future advancements is vast, and research continues to uncover new and innovative applications for these molecules.
Questions Often Asked: Amoeba Sisters Video Recap Answers Dna Vs Rna
What are the key structural differences between DNA and RNA?
DNA is a double-stranded molecule, while RNA is single-stranded. DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose, while RNA contains ribose. DNA has the nitrogenous bases adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine, while RNA has adenine, uracil, guanine, and cytosine.
What is the role of DNA in transcription?
DNA serves as the template for transcription, the process by which RNA is synthesized. During transcription, an enzyme called RNA polymerase binds to the DNA and separates the two strands. The RNA polymerase then uses one of the DNA strands as a template to create a complementary RNA molecule.
What is the role of RNA in translation?
RNA plays a crucial role in translation, the process by which proteins are synthesized. During translation, ribosomes bind to mRNA and use the mRNA sequence to determine the order of amino acids in the protein.