Coalesced type of skin lesion configuration, characterized by the merging of individual lesions into larger, interconnected patches, presents a unique set of clinical challenges and diagnostic considerations. This article delves into the intricacies of coalesced skin lesions, providing healthcare professionals with a comprehensive understanding of their significance, differential diagnosis, and management.
Coalesced skin lesions often indicate the progression or severity of underlying skin conditions, necessitating prompt and accurate diagnosis. Understanding the characteristic features and potential complications associated with coalesced lesions is paramount for effective patient care.
1. Coalesced Skin Lesions
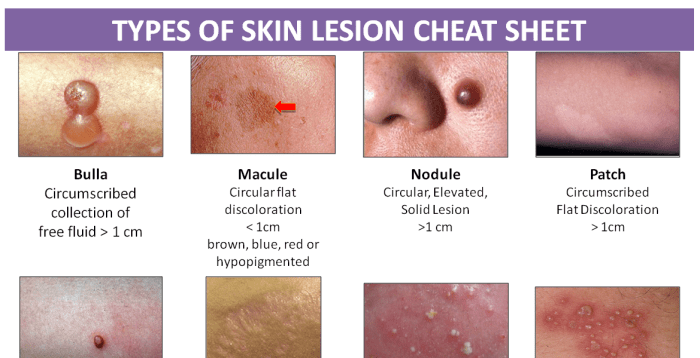
Coalesced skin lesions occur when multiple, closely situated lesions merge or grow together to form a larger, interconnected lesion. This type of lesion configuration is often seen in various skin conditions and can have clinical significance in indicating the severity and potential complications of the underlying disease.
Typical Characteristics
- Multiple, closely spaced lesions
- Lesions that have fused or merged together
- Irregular borders
- Increased size and extent compared to individual lesions
Examples
- Erythema multiforme
- Psoriasis
- Atopic dermatitis
- Herpes simplex virus infection
2. Clinical Significance of Coalesced Lesions
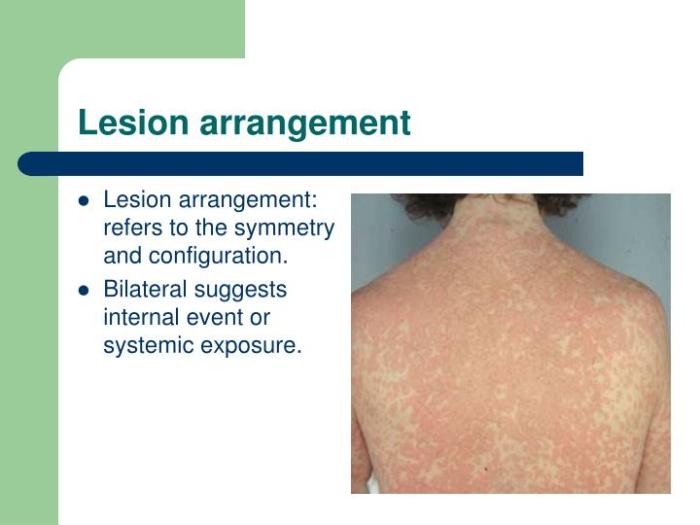
Coalesced skin lesions can have significant clinical implications in the evaluation and management of skin conditions. Their presence can indicate:
Severity of Disease
- Coalesced lesions often indicate a more severe or advanced stage of a skin condition.
- The extent of coalescence can correlate with the intensity of the inflammatory response and the underlying disease activity.
Potential Complications, Coalesced type of skin lesion configuration
- Coalesced lesions can increase the risk of secondary infections due to compromised skin integrity.
- They may lead to scarring and disfigurement if not treated promptly and effectively.
3. Differential Diagnosis of Coalesced Lesions
Differentiating between different skin conditions that can cause coalesced lesions is crucial for appropriate management. The following table summarizes the key features of some common conditions:
| Condition | Morphology | Distribution | Associated Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Erythema multiforme | Target lesions, coalescing into larger plaques | Acral distribution | Fever, malaise |
| Psoriasis | Thickened, scaly plaques | Extensor surfaces, scalp | Itching, pain |
| Atopic dermatitis | Eczematous lesions, coalescing into plaques | Flexural areas | Intense itching, dryness |
| Herpes simplex virus infection | Vesicular lesions, coalescing into clusters | Perioral, genital | Pain, itching, tingling |
Biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and exclude other potential causes.
4. Management of Coalesced Lesions
The management of coalesced skin lesions depends on the underlying skin condition. General principles include:
Treatment of Underlying Condition
- Treating the underlying skin condition is essential to address the root cause of the lesions.
- This may involve topical or systemic medications, phototherapy, or other therapeutic modalities.
Prevention of Complications
- Preventing secondary infections is crucial by maintaining good skin hygiene and using topical antibiotics if necessary.
- Emollients and moisturizers can help protect the skin barrier and reduce inflammation.
Top FAQs: Coalesced Type Of Skin Lesion Configuration
What is the definition of coalesced skin lesions?
Coalesced skin lesions are characterized by the merging of individual lesions into larger, interconnected patches.
What are the typical characteristics of coalesced skin lesions?
Coalesced skin lesions often appear as irregular, confluent patches with indistinct borders and may exhibit changes in color, texture, and elevation.
What are some examples of skin conditions that can cause coalesced lesions?
Coalesced skin lesions can be associated with a wide range of skin conditions, including eczema, psoriasis, and infectious diseases.