Pine needle cross section labeled provides a comprehensive understanding of the internal structure and key features of pine needles. This detailed analysis unveils the arrangement of cells, allowing for insights into plant physiology, ecology, and evolution.
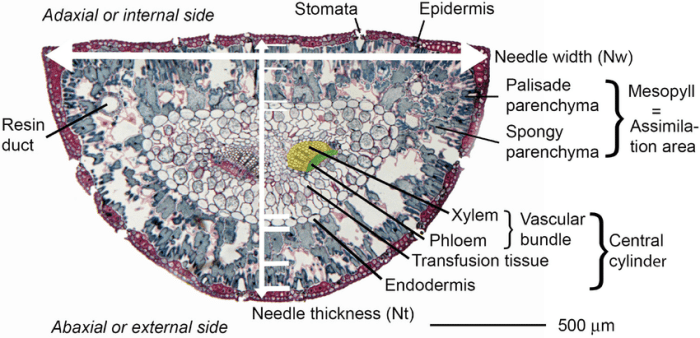
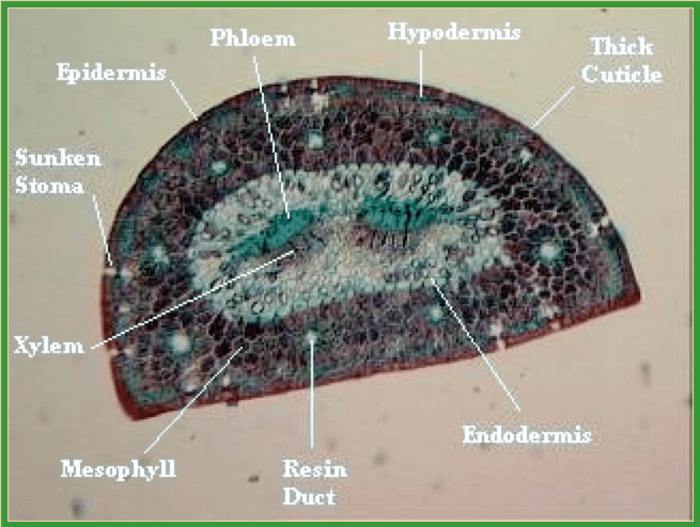
The cross section reveals the distinct layers of a pine needle, including the epidermis, mesophyll, and vascular bundles. Each layer comprises specialized cells with unique functions, contributing to the overall functionality and adaptation of the pine needle to its environment.
Pine Needle Anatomy
Pine needles are the primary photosynthetic organs of pine trees and are composed of various tissues arranged in a specific manner. The structure of a pine needle can be examined through cross-section analysis, which provides insights into the arrangement and function of different cell types.
Types of Cells in a Pine Needle
Pine needles contain several types of cells, including:
- Epidermal cells: These cells form the outer layer of the needle and protect the underlying tissues from external factors.
- Parenchyma cells: These cells are responsible for photosynthesis and storage of nutrients.
- Transfusion tracheids: These cells are responsible for transporting water and minerals throughout the needle.
- Resin canals: These channels contain resin, which provides defense against insects and pathogens.
Arrangement of Cells in a Pine Needle Cross Section
In a cross section of a pine needle, the cells are arranged in a concentric pattern around a central vascular bundle:
- Epidermis: The outermost layer of the needle, consisting of a single layer of epidermal cells.
- Hypodermis: A layer of parenchyma cells located beneath the epidermis, containing chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
- Endodermis: A layer of cells surrounding the vascular bundle, responsible for regulating water and nutrient transport.
- Vascular bundle: The central core of the needle, consisting of xylem (for water transport) and phloem (for nutrient transport).
Cross Section Preparation: Pine Needle Cross Section Labeled
Proper preparation of pine needle cross sections is crucial for obtaining clear and informative images. Here are the steps involved:
- Sample collection:Collect healthy, mature pine needles from the tree.
- Fixation:Preserve the needles in a fixative solution to prevent cell damage.
- Embedding:Embed the needles in a paraffin or plastic resin to support the tissue during sectioning.
- Sectioning:Use a microtome to cut thin sections (typically 5-10 micrometers) perpendicular to the needle’s long axis.
- Staining:Stain the sections with dyes to enhance the visibility of different cell types and structures.
Importance of Proper Sample Preparation
Proper sample preparation ensures:
- Preservation of cell structures and relationships
- Obtaining clear and interpretable cross sections
- Accurate identification and analysis of cell types and features
Cross Section Examination
Cross sections of pine needles can be examined using various methods:
- Light microscopy:A standard technique that uses visible light to visualize the cross section.
- Fluorescence microscopy:Uses fluorescent dyes to highlight specific cell components or structures.
- Electron microscopy:Provides high-resolution images of the cross section at the ultrastructural level.
Microscopy in Pine Needle Cross Section Analysis
Microscopy plays a crucial role in pine needle cross section analysis by allowing researchers to:
- Identify and characterize different cell types
- Study the arrangement and distribution of cells
- Examine cellular structures and organelles
- Analyze changes in cell morphology and physiology under different conditions
Guidelines for Interpreting Cross Section Features
When examining pine needle cross sections, it is important to:
- Use a calibrated microscope and appropriate magnification.
- Identify key features such as cell shape, size, and arrangement.
- Correlate observations with known anatomical structures and functions.
- Consider the potential for artifacts or distortions due to sample preparation.
Key Features of a Pine Needle Cross Section
Key features visible in a pine needle cross section include:
- Epidermis:A single layer of cells forming the outer boundary of the needle.
- Hypodermis:A layer of parenchyma cells containing chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
- Endodermis:A layer of cells surrounding the vascular bundle, responsible for regulating water and nutrient transport.
- Vascular bundle:The central core of the needle, consisting of xylem (for water transport) and phloem (for nutrient transport).
- Resin canals:Channels containing resin, which provides defense against insects and pathogens.
Significance of Key Features
These features play important roles in the function and survival of pine needles:
- Epidermis: Protects the needle from desiccation and pathogens.
- Hypodermis: Conducts photosynthesis, providing energy for the needle.
- Endodermis: Regulates water and nutrient uptake, ensuring optimal growth and development.
- Vascular bundle: Transports water and nutrients throughout the needle.
- Resin canals: Provide defense against herbivores and pathogens.
| Feature | Function |
|---|---|
| Epidermis | Protection from desiccation and pathogens |
| Hypodermis | Photosynthesis |
| Endodermis | Regulation of water and nutrient uptake |
| Vascular bundle | Transport of water and nutrients |
| Resin canals | Defense against herbivores and pathogens |
Applications of Pine Needle Cross Section Analysis
Pine needle cross section analysis has applications in various fields:
- Plant physiology:Studying water and nutrient transport, photosynthesis, and defense mechanisms.
- Ecology:Assessing environmental stress, pollution tolerance, and plant-herbivore interactions.
- Evolution:Comparing anatomical structures across different pine species to understand evolutionary relationships.
Examples of Studies Utilizing Pine Needle Cross Section Analysis, Pine needle cross section labeled
- A study used cross section analysis to examine the effects of drought stress on water transport in pine needles.
- Another study analyzed the cross sections of pine needles from polluted environments to assess the impact of air pollution on needle anatomy.
- A comparative study used cross section analysis to identify anatomical differences between different pine species, providing insights into their evolutionary relationships.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of the epidermis in a pine needle cross section?
The epidermis, the outermost layer of the pine needle, plays a crucial role in protecting the inner tissues from environmental stresses and regulating water loss through its waxy cuticle.
How can cross section analysis aid in understanding plant evolution?
Cross section analysis provides comparative data on the structural variations among different pine species, allowing researchers to trace evolutionary relationships and infer adaptation patterns over time.